INDICATION
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
INDICATION
OJJAARA is indicated for the treatment of intermediate or high-risk myelofibrosis (MF), including primary MF or secondary MF [post-polycythemia vera (PV) and post-essential thrombocythemia (ET)], in adults with anemia.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Risk of Infections
- Serious (including fatal) infections (e.g., bacterial and viral, including COVID-19) occurred in 13% of patients treated with OJJAARA. Infections regardless of grade occurred in 38% of patients. Delay starting therapy until active infections have resolved. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of infection and initiate appropriate treatment promptly.
Hepatitis B Reactivation
- Hepatitis B viral load (HBV-DNA titer) increases, with or without associated elevations in alanine transaminase (ALT) or aspartate transaminase (AST), have been reported in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection taking Janus Kinase (JAK) inhibitors, including OJJAARA. The effect of OJJAARA on viral replication in patients with chronic HBV infection is unknown. In patients with HBV infections, check hepatitis B serologies prior to starting OJJAARA. If HBsAg and/or anti-HBc antibody is positive, consider consultation with a hepatologist regarding monitoring for reactivation versus prophylactic hepatitis B therapy. Patients with chronic HBV infection who receive OJJAARA should have their chronic HBV infection treated and monitored according to clinical HBV guidelines.
Thrombocytopenia and Neutropenia
- New or worsening thrombocytopenia, with platelet count less than 50 × 109/L, was observed in 20% of patients treated with OJJAARA. Eight percent of patients had baseline platelet counts less than 50 × 109/L.
- Severe neutropenia, absolute neutrophil count (ANC) less than 0.5 × 109/L, was observed in 2% of patients treated with OJJAARA.
- Assess complete blood counts (CBC), including platelet and neutrophil counts, before initiating treatment and periodically during treatment as clinically indicated. Interrupt dosing or reduce the dose for thrombocytopenia or neutropenia.
Hepatotoxicity
- Two of the 993 patients with MF who received at least one dose of OJJAARA in clinical trials experienced reversible drug-induced liver injury. Overall, new or worsening elevations of ALT and AST (all grades) occurred in 23% and 24%, respectively, of patients treated with OJJAARA; Grade 3 and 4 transaminase elevations occurred in 1% and 0.5% of patients, respectively. New or worsening elevations of total bilirubin occurred in 16% of patients treated with OJJAARA. All total bilirubin elevations were Grades 1-2. The median time to onset of any grade transaminase elevation was 2 months, with 75% of cases occurring within 4 months.
- Delay starting therapy in patients presenting with uncontrolled acute and chronic liver disease until apparent causes have been investigated and treated as clinically indicated. When initiating OJJAARA, refer to dosing in patients with hepatic impairment.
- Monitor liver tests at baseline, every month for 6 months during treatment, then periodically as clinically indicated. If increases in ALT, AST or bilirubin related to treatment are suspected, modify OJJAARA dosage based upon Table 1 within the Prescribing Information.
Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions (SCARs)
- Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs), including toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), have been observed in some patients treated with OJJAARA.
- If signs or symptoms of SCARs occur, interrupt OJJAARA until the etiology of the reaction has been determined. Consider early consultation with a dermatologist for evaluation and management.
- If etiology is considered to be associated with OJJAARA, permanently discontinue OJJAARA and do not reintroduce OJJAARA in patients who have experienced SCARs or other life-threatening cutaneous reactions during treatment with OJJAARA.
Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events (MACE)
- Another JAK inhibitor increased the risk of MACE, including cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, and stroke [compared with those treated with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blockers] in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, a condition for which OJJAARA is not indicated.
- Consider the benefits and risks for the individual patient prior to initiating or continuing therapy with OJJAARA, particularly in patients who are current or past smokers and patients with other cardiovascular risk factors. Inform patients receiving OJJAARA of the symptoms of serious cardiovascular events and the steps to take if they occur.
Thrombosis
- Another JAK inhibitor increased the risk of thrombosis, including deep venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and arterial thrombosis (compared with those treated with TNF blockers) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, a condition for which OJJAARA is not indicated. Evaluate patients with symptoms of thrombosis and treat appropriately.
Malignancies
- Another JAK inhibitor increased the risk of lymphoma and other malignancies excluding nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC) (compared with those treated with TNF blockers) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, a condition for which OJJAARA is not indicated. Current or past smokers were at increased risk.
- Consider the benefits and risks for the individual patient prior to initiating or continuing therapy with OJJAARA, particularly in patients with a known malignancy (other than a successfully treated NMSC), patients who develop a malignancy, and patients who are current or past smokers.
Adverse Reactions
- The most common adverse reactions (≥20% in either study) are thrombocytopenia, hemorrhage, bacterial infection, fatigue, dizziness, diarrhea, and nausea.
Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptide (OATP)1B1/B3 Inhibitors
- Momelotinib is an OATP1B1/B3 substrate. Concomitant use with an OATP1B1/B3 inhibitor increases momelotinib maximal concentrations (Cmax) and area under the concentration-time curve (AUC), which may increase the risk of adverse reactions with OJJAARA. Monitor patients concomitantly receiving an OATP1B1/B3 inhibitor for adverse reactions and consider OJJAARA dose modifications.
Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (BCRP) Substrates
- Momelotinib is a BCRP inhibitor. OJJAARA may increase exposure of BCRP substrates, which may increase the risk of BCRP substrate adverse reactions. When administered concomitantly with OJJAARA, initiate rosuvastatin (BCRP substrate) at 5 mg and do not increase to more than 10 mg once daily. Dose adjustment of other BCRP substrates may also be needed. Follow approved product information recommendations for other BCRP substrates.
Pregnancy
- Available data in pregnant women are insufficient. OJJAARA should only be used during pregnancy if the expected benefits to the mother outweigh the potential risks to the fetus.
Lactation
- It is not known whether OJJAARA is excreted in human milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child, patients should not breastfeed during treatment with OJJAARA, and for at least 1 week after the last dose of OJJAARA.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
- Advise females of reproductive potential who are not pregnant to use highly effective contraception during therapy and for at least 1 week after the last dose of OJJAARA.
Hepatic Impairment
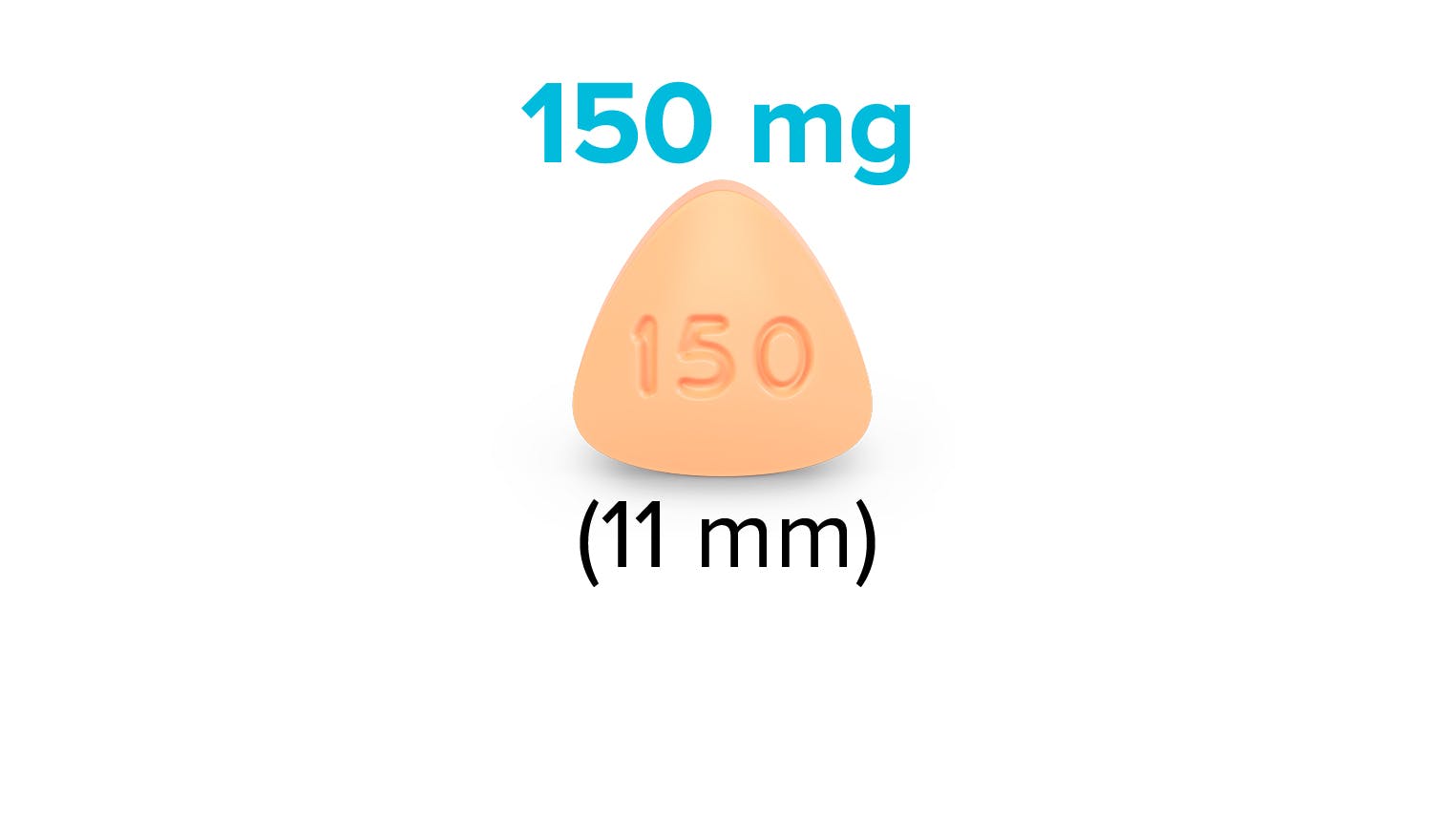
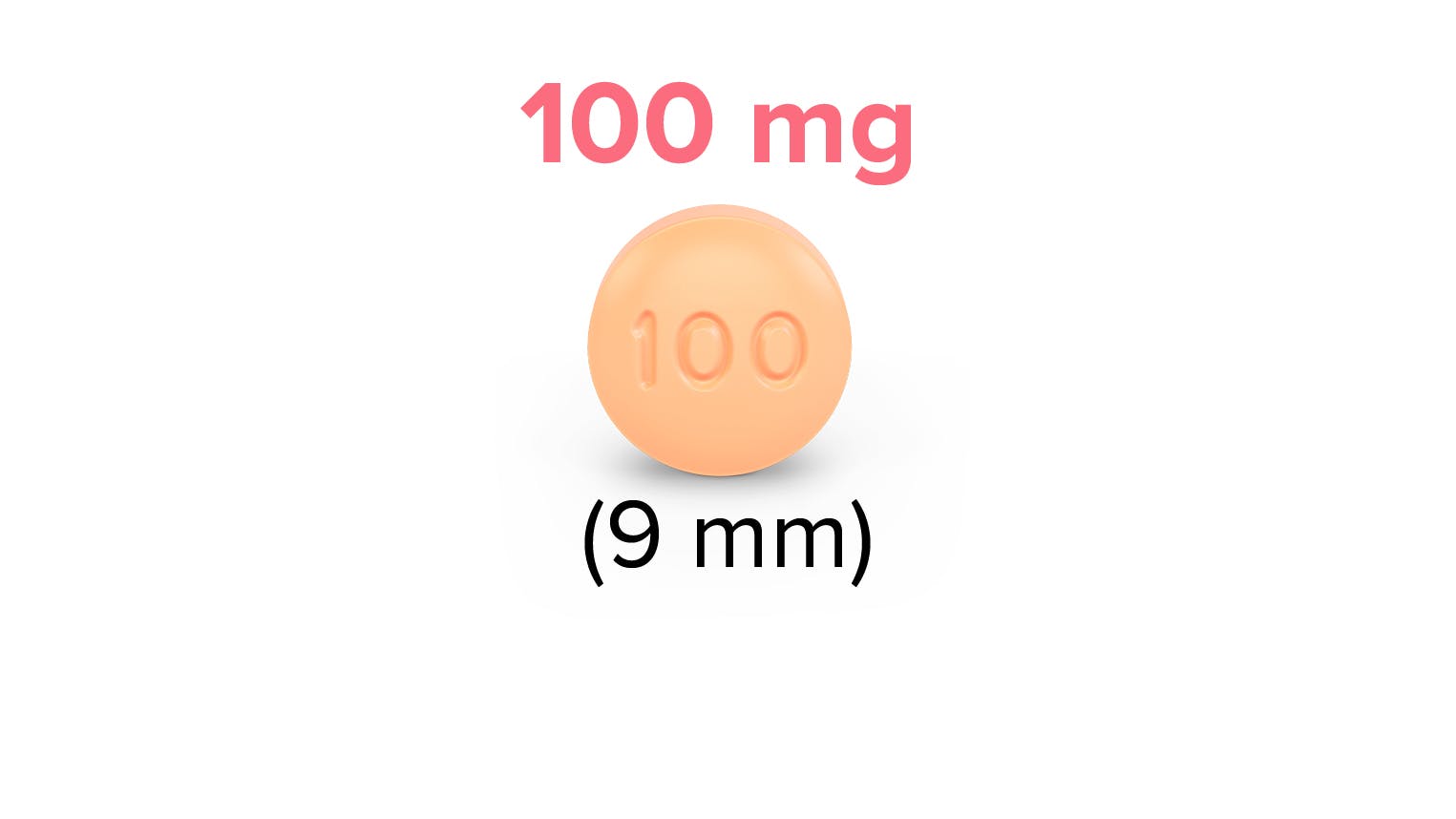
- Momelotinib exposure increased with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C). The recommended starting dose of OJJAARA in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) is 150 mg orally once daily. No dose modification is recommended for patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A) or moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B).
Please see full Prescribing Information for OJJAARA.